Overview Of Autoimmune Disease In Common Variable Immunodeficiency
The initial clustering of CVID patients with autoimmunity included organ specific autoimmune disease , systemic autoimmune disease , and autoimmune cytopenias . Further analysis on two other cohorts showed that within the autoimmune cluster, only autoimmune cytopenias had decreased survival and that organ-specific and systemic autoimmune disease showed no association with cytopenias or the other clinical phenotypes . This led to a revision of the clinical phenotypes with more emphasis being placed on autoimmune cytopenias as opposed to autoimmunity in general . Unbiased network clustering in a separate CVID cohort yielded similar phenotypes, with systemic and organ-specific autoimmune diseases clustering separately from autoimmune cytopenias . While this distinction likely carries implications regarding underlying pathophysiology, many studies continue to combine autoimmune cytopenias with other autoimmunity as they compare CVID patients. For this reason, we will make distinctions between autoimmune cytopenias and organ specific or systemic autoimmunity in this review.
Infusion Therapy For Primary Immunodeficiency
Infusion therapy provides a viable treatment option for patients for whom an underlying medical condition makes it difficult or impossible to swallow oral medications. It also offers an alternative for people who have failed to obtain relief from oral drugs. And, since the medication is injected directly into the bloodstream, patients typically experience alleviated symptoms at a much faster rate.
Celiac Disease Markers In Psoriasis
Seven studies have reported a positive association between psoriasis and celiac disease markers . All of these studies compared a group of psoriasis patients to a non-psoriatic control group, with the number of psoriasis patients ranging from 37 to 302. Ojetti et al. evaluated 92 consecutive psoriasis patients seen in an Italian dermatology department for the presence of celiac disease antibodies compared to 90 healthy controls. Four of the 92 psoriasis patients were diagnosed with celiac disease based on positivity for IgA EMA antibodies and confirmatory small bowel biopsies showing villous atrophy, compared to none of 90 controls . A Swedish study of 302 patients with psoriasis and 99 reference subjects found that psoriasis patients had elevated IgA AGA levels compared to the reference group, but that IgG AGA did not differ. Four additional studies in Turkey, Egypt, Poland, and India also found elevated IgA AGA levels in psoriasis patients compared to controls, and also elevated IgA tTG levels in the latter two studies. Beyond serological testing, a case-control study found that malabsorption was present in 60% of psoriatic patients and only 3% of controls.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Prevent Psoriasis
Psoriatic Disease Affects More Than Skin And Joints
The systemic inflammation that drives symptoms of psoriatic disease can raise your risk for other health problems.
If you have psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis , you may know that these diseases raise your risk for some other conditions as well. When one disease is triggered by or linked to another, the related condition is called a âcomorbidity.â PsA, for example, is a common comorbidity of psoriasis, affecting up to 33 percent of people with psoriasis.
According to the recent Joint AAD-NPF Guidelines of Care for the Management and Treatment of Psoriasis with Awareness and Attention to Comorbidities, other comorbidities for which psoriatic disease raises risk include:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Mental health impacts, including depression and anxiety
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Uveitis
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Just how this elevated risk happens for each comorbidity isnât fully understood. One underlying factor that likely plays an important role in triggering or contributing to development of many comorbidities, however, is systemic inflammation, explains dermatologist Paul S. Yamauchi, M.D., Ph.D.
The weapons the immune system uses for this attack are inflammatory immune cells that normally defend the body from injury and infection.
How Is Pidd Treated
PIDD treatment will depend on which disease you have. Once diagnosed, you can manage the disease by working with your doctor to develop a treatment plan.
Treatment often starts with preventing and treating infections and boosting the immune system. Any infection should be treated promptly and aggressively. Patients may need mucus thinners, cough syrup or decongestants to relieve symptoms caused by infections. If the infection doesnt respond to oral antibiotics, then hospitalization and IV antibiotics may be necessary.
Some PIDD patients may be prescribed long-term antibiotics to prevent infections and avoid potential damage to the lungs or ears .
Another option for some is a stem cell transplant, which offers a permanent cure for several forms of PIDD. With this treatment, healthy stem cells are transferred to the person with immunodeficiency, offering anormally functioning immune system.
Gene therapy is an option for severe PIDD patients. Most PIDDs are caused by errors in specific genes, and with gene therapy its hoped that fixing these mutations can help to correct the PIDD.
Patients can boost their immune system with therapies designed to fight bacterial and viral infections by antibody replacement. The most common is IV or subcutaneous immunoglobulin infusions these are mostlyprescribed for antibody deficiency.
Read Also: Does Aloe Vera Help Psoriasis
Introduction And General Principles
Individuals may be immunocompromised as a result of a congenital condition, an illness or medications that suppress immune function. In general, immunocompromised persons are more susceptible to vaccine-preventable infections and may have severe infections. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines in immunocompromised persons are determined by the type of immunodeficiency and degree of immunosuppression. Each immunocompromised person is different and presents unique considerations regarding immunization. The relative degree of immunodeficiency is variable depending on the underlying condition, the progression of disease and use of immunosuppressive agents. Immunodeficiency can also vary over time in many people and the decision to recommend for or against a particular vaccine will depend upon a case-by-case analysis of the risks and benefits. There is potential for serious illness and death if immunocompromised people are under-immunized and every effort should be made to ensure adequate protection through immunization however, inappropriate use of live vaccines can cause serious adverse events in some immunocompromised people as a result of uncontrolled replication of the vaccine virus or bacterium.
The following recommendations reflect general best practices and are subject to individual considerations and new evidence as it arises.
Interpretation Provides Information To Assist In Interpretation Of The Test Results
Evaluation and categorization of variants is performed using the most recent published American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics recommendations as a guideline. Variants are classified based on known, predicted, or possible pathogenicity and reported with interpretive comments detailing their potential or known significance.
Multiple in silico evaluation tools may be used to assist in the interpretation of these results. The accuracy of predictions made by in silico evaluation tools is highly dependent upon the data available for a given gene, and predictions made by these tools may change over time. Results from in silico evaluation tools should be interpreted with caution and professional clinical judgment.
Read Also: Psoriasis On Hands And Feet Treatment
List Of Some Autoimmune Disorders
Primary immune deficiency diseases are those caused by inherited genetic mutations. Secondary or acquired immune deficiencies are caused by something outside the body such as a virus or immune suppressing drugs.
Primary immune diseases are at risk to an increased susceptibility to, and often recurrent ear infections, pneumonia, bronchitis, sinusitis or skin infections. Immunodeficient patients may less frequently develop abscesses of their internal organs, autoimmune or rheumatologic and gastrointestinal problems.
- Primary immune deficiencies
- Hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome
- Common variable immunodeficiency : B-cell levels are normal in circulation but with decreased production of IgG throughout the years, so it is the only primary immune disorder that presents onset in the late teens years.
- Chronic granulomatous disease : a deficiency in NADPH oxidase enzyme, which causes failure to generate oxygen radicals. Classical recurrent infection from catalase positive bacteria and fungi.
- Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome
- Hyper IgM syndrome: X-linked disorder that causes a deficiency in the production of CD40 ligand on activated T-cells. This increases the production and release of IgM into circulation. The B-cell and T-cell numbers are within normal limits. Increased susceptibility to extracellular bacteria and opportunistic infections.
Disturbances Of B Cells
The total number of peripheral B cells is slightly reduced in about 40 to 50% of CVID patients . In some patients elevated numbers of B cells are reported, often associated with polyclonal lymphoid organ infiltration and autoimmunity . In only about 10% of CVID patients are B cells dramatically reduced or absent . Disease progression tends to be more rapid and severe in these patients and the X-linked form of agammaglobulinemia and Good’s syndrome have to be excluded .
In 2008 a European multi-center trial combined both classification systems and proposed the EUROclass classification . B cells were phenotyped for CD19, IgD/IgM, CD27, CD21 and CD38 expression patients with more than 1% circulating B cells were distinguished from those with less than 1% . The B+ group was further split into patients with normal or reduced percentages of switched memory B cells . Further subgroups were established depending on the expansion of CD21low B cells or transitional B cells. The EUROclass trial confirmed the clinical association of reduced switched memory B cells and expanded CD21low B cells with splenomegaly and granulomatous disease and revealed for the first time an expansion of transitional B cells in patients with lymphadenopathy .
Read Also: Best Bath Soak For Psoriasis
Diseases Of Immune Dysregulation
In certain conditions, the regulation rather than the intrinsic activity of parts of the immune system is the predominant problem.
- X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome
- Syndromes with autoimmunity:
- Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome: type 1a , type 1b , type 2a , type 2b
- APECED
- IPEX
- CD25 deficiency
Caspase Eight Deficiency State
Caspase eight deficiency state, or CEDS, is a very rare genetic disorder of the immune system caused by mutations in the CASP8 gene. CEDS is characterized by an enlarged spleen and lymph nodes, recurrent sinus and lung infections, recurrent viral infections, and a low level of infection-fighting antibodies. NIH researchers first described this condition in two siblings in 2002. .
Also Check: Start Of Psoriasis On Elbow
Microbiome In Cvid And Autoimmunity
As noted above, monogenic mutations represent a minority of CVID patients with CVID. The majority of cases may be polygenic, or perhaps better defined as simply multifactorial, with environmental, epigenetic, or other factors contributing. Over the past decade, the microbiome has been implicated in the manifestation of immune dysregulation , and has been explored in the pathogenesis of CVID complications .
It has been hypothesized that impaired immunity results in increased microbial translocation across the gut barrier. This in turn drives persistent systemic immune activation leading to the disruption of the immune homeostasis . While regular immune sampling and microbial translocation occur in healthy individuals , the increased frequency occurring in CVID patients with diminished barrier function may lead to both local and systemic inflammation and immune dysregulation. Lipopolysaccharides and soluble CD14 and IL-2 are used as markers for endotoxemia since their presence in systemic circulation is indicative of increased gut microbial translocation . CVID patients have higher levels of LPS and soluble CD14 and IL-2 compared to healthy controls, and CVID patients with autoimmune complications have higher levels compared to CVID without complications .
B Cell Dysfunction In Cvid Autoimmune Disease

Low frequency of TR cells in CVID patients with autoimmunity is associated with expansion of a particular B cell type, CD21low B cell , linking T and B cell pathology in CVID. Early studies have shown that reduced switched memory B cell percentage correlates more strongly with autoimmunity in patients with CVID compared to serum IgG levels . Indeed, patients with reduced numbers of switched memory B cells had greater than a 3-fold increase in their risk of autoimmune cytopenias and systemic autoimmune disease . Subsequent studies found increased proportions of CD21low B cells in patients with CVID , with clustering of these low levels in patients with autoimmunity . Interestingly, non-CVID patients with autoimmune disease have also been found to have expansion of CD21low B cells . These cells were found to have preferential homing to peripheral tissues such as the synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients and the bronchoalveolar space of CVID patients . Further analysis found that CD21low B cells from both rheumatoid arthritis and CVID patients expressed germline autoreactive antibodies which recognized nuclear and cytoplasmic structures . Authors concluded that CD21low B cells are a distinct, polyclonal, pre-activated, partially autoreactive, functionally attenuated B cell population with preferential enrichment in peripheral tissues thus offering another possible mechanism of autoimmunity in patients with CVID .
Read Also: How To Cure Psoriasis On Feet
Crohns Disease Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Crohns disease and celiac disease share many common symptoms, though the underlying causes are different. In Crohns disease, the immune system could be causing disruption anywhere along the gastrointestinal tract, and more diagnostic testing is needed to establish a diagnosis compared to celiac disease. Treatment consists of diet changes and possible surgery. A substantial overlap of patients with these two conditions suggests there may be a genetic connection between the two, and research is continuing in that area.
There Are Many Types Of Pi They All Affect The Immune System
Primary immunodeficiency is a term used to describe more than 350 disorders. Although they all have differences, what these disorders all have in common is that they cause the immune system to not work right, in some cases making it harder to fight off infections. PI is a chronic disorder that causes your immune system to work improperly. This leads to increased chance of an infection. And because the types of infections can vary, diagnosing PI can be difficult.
Don’t Miss: How To Stop Guttate Psoriasis Spreading
F How Do We Document And Evaluate Hiv Infection
Any individual with HIV infection, including one with a diagnosis of acquired immune deficiency syndrome , may be found disabled under 14.11 if his or her impairment meets the criteria in that listing or is medically equivalent to the criteria in that listing.
1. Documentation of HIV infection.
a. Definitive documentation of HIV infection. We may document a diagnosis of HIV infection by positive findings on one or more of the following definitive laboratory tests:
HIV antibody screening test , confirmed by a supplemental HIV antibody test such as the Western blot , an immunofluorescence assay, or an HIV-1/HIV-2 antibody differentiation immunoassay.
HIV nucleic acid detection test .
HIV p24 antigen test.
Isolation of HIV in viral culture.
Other tests that are highly specific for detection of HIV and that are consistent with the prevailing state of medical knowledge.
b. We will make every reasonable effort to obtain the results of your laboratory testing. Pursuant to §§ 404.1519f and 416.919f, we will purchase examinations or tests necessary to make a determination in your claim if no other acceptable documentation exists.
c. Other acceptable documentation of HIV infection. We may also document HIV infection without definitive laboratory evidence.
2. Documentation of the manifestations of HIV infection.
c. Other acceptable documentation of manifestations of HIV infection. We may also document manifestations of HIV infection without definitive laboratory evidence.
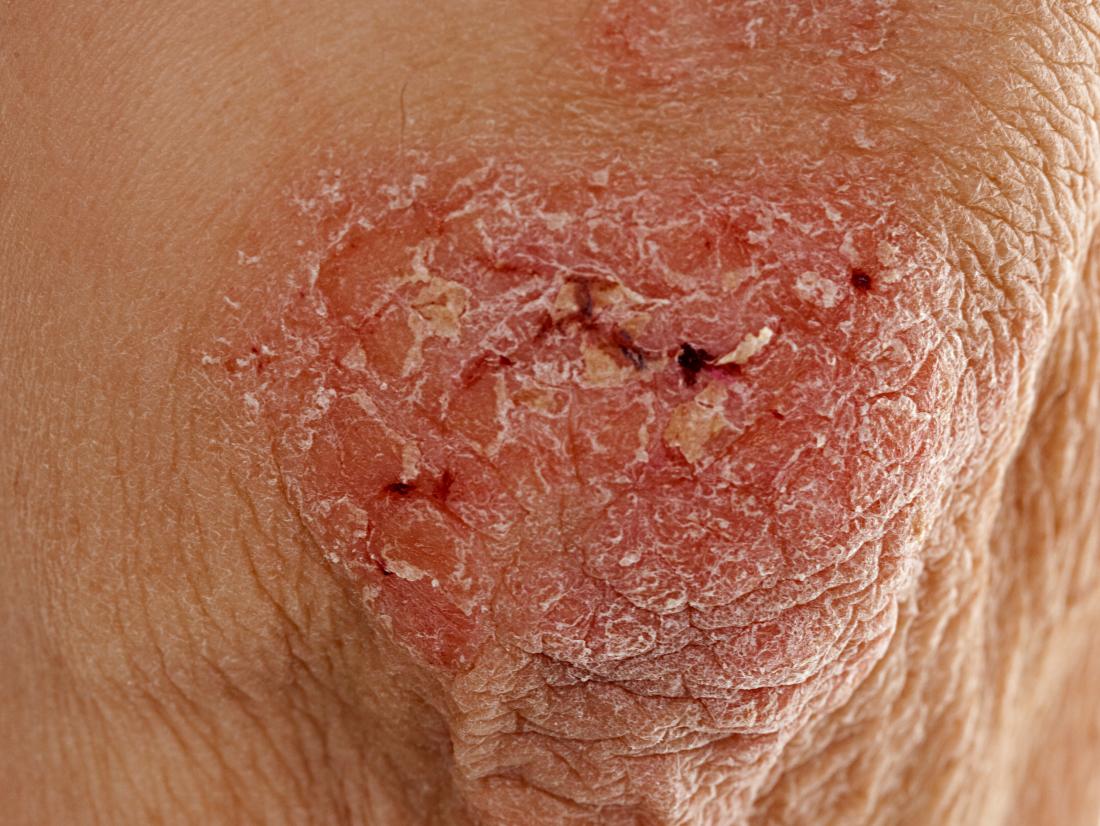
Why Is Psoriasis An Autoimmune Disorder
As part of its defense against foreign invaders, your body makes specialized white blood cells called T-cells. Under normal circumstances, T-cells identify and coordinate attacks on foreign invaders.
However, when you have psoriasis, your T-cells mistakenly identify your skin cells as invaders and attack them. This attack injures the skin cells, setting off a cascade of responses in your immune system and in your skin, resulting in the skin damage seen in psoriasis swelling, reddening, and scaling.
In an effort to heal, your skin cells begin reproducing much more rapidly than normal, and large numbers of new skin cells push their way to the surface of your skin. This occurs so quickly that older skin cells and white blood cells aren’t shed quickly enough. These discarded cells pile up on the surface of the skin, creating thick, red plaques with silvery scales on their surface: the hallmark of the classic form of plaque psoriasis.
You May Like: How Fast Does Psoriasis Spread
The Role Of Inflammation
Inflammation is an important reaction to infection, injuries, and toxins. When the immune response of the body is triggered in cases of psoriatic disease, it can lead to inflammation that can cause skin and/or joint symptoms to flare , along with systemic inflammation that can affect other parts of the body.
Normally, it takes 21 to 28 days for cells on the surface of the skin to grow and shed it may take as few as four days in skin affected by psoriasis, due to the increased immune response. For psoriasis, a flare may include new psoriasis plaques or the return of plaques to a prior location, itch, irritation, or burning.
With PsA, a flare may include new or increased pain, tenderness, swelling, or stiffness in joints. Flares may last for various amounts of time and may vary in level of severity.
However, having skin affected by psoriasis or joints affected by PsA can be a sign of inflammation occurring in other parts of the body. Even people living with mild psoriasis may have inflammation in the body.
Are There Certain Conditions That Make You More Susceptible
From the available data, individuals over 70 and those with any chance of lung disease are at a higher risk, explains Ballow. We have a lot more patients on biologics for IBD, psoriasis, and autoimmune hemo anemia , which suppress the immune system, he notes.
The more severe or potentially life- or organ-threatening rheumatic diseases, such as lupus, systemic vasculitis, and severe forms of rheumatoid arthritis, may require stronger or higher doses of medication, Roberts explains.
These medications suppress the immune system to a greater degree, exposing the individual to greater risks due to infections, he says. Sometimes these conditions and medications may make it difficult to detect infections, since patients may not exhibit the normal symptoms of infections, such as high fevers or high white blood cell counts. Roberts explains that any unusual or unfamiliar symptom in these patients should be viewed with suspicion.
Also Check: Best Cure For Psoriasis On Hands