What Is The Difference Between Seborrheic Dermatitis And Scalp Eczema
Both present very similarly. They can both have large scalp flakes and scaling along with raised patches of skin that is red and flaky. These patches can be yellow or white in color. They can be bleeding or they can be itchy. But one of the main things that separates these two skin problems is whether the skin on the head is oily or dry. If you are having oily or greasy problems then it is most likely seborrhea or seborrheic dermatitis. Many times it will also be characterized on the face, behind the ears, eyebrows and on the cheeks as redness, scaling, flaking and more. It will also present in the corners of the mouth and around the creases of the nose. Sometimes it will be present in other places as well. However, note that if you would characterize it along with greasy or oily dandruff then it is most likely seborrheic dermatitis.
If your skin or the patches appear or feel dry to the touch but also seem very similar to raised, red, flaking patches on the scalp then these are most likely eczema. There can be seborrheic eczema diagnosis given but we believe that is the same as dermatitis. Remember that the word dermatitis just basically means the skin is irritated.
How Do You Get Rid Of Seborrheic Dermatitis On The Scalp Naturally
Its best to work with your dermatologist to treat seborrheic dermatitis since this condition can be chronic and recur in some people. To help manage the itching on your own, you can try home remedies like a gentle moisturizer, unscented skin products, lukewarm baths or showers, coconut oil, tea tree oil, and stress management techniques.
What Are Scalp Psoriasis Symptoms And Signs Can Scalp Psoriasis Cause Hair Loss
Psoriasis appears as a small bump, a papule, surmounted by scale. When these papules coalesce, a plaque is formed that is often covered by thick layers of horny scale. When this scale is shed, it appears as dandruff, which can be quite unsightly. Scratching these plaques, either because of itching or because of the impulse to remove it, is a very poor idea because of what is called the Koebner phenomenon . This may cause psoriasis to develop in areas of inflammation and trauma. Scratching off the scale will only make things worse. Although most patients do not note hair loss, there can be extensive alopeciahair loss in severe cases.
Also Check: Can Econazole Nitrate Cream Be Used For Psoriasis
What Is Scalp Psoriasis When Can Scalp Psoriasis Begin
Psoriasis is an inflammatory disease of the skin that is estimated to affect about 2.2% of the adult population. In children, the onset of psoriasis can be before the age of one year but peaks around 5-8 years. Psoriasis produces scaly, itchingbumps on the skin. Some people may have a genetic predisposition to psoriasis. The genes affected seem to be involved with control of the immune system. Psoriasis appears as red scaling, slightly raised bumps that merge to form plaques. Psoriasis classically appears on the elbows and knees, but it can affect any part of the skin. The scalp is also characteristically affected in many people. Like psoriasis anywhere on the body, scalp plaques produce excess scale and can itch. Severe disease can cause a loss of scalp hair, which usually will return if the disease can be controlled. Scalp psoriasis somewhat difficult to treat when the scalp is covered with hair sufficient to act a barrier to the application of topical medications.
It Can Affect The Scalp Hairline Forehead Back Of The Neck And Skin Around The Ears
Did You Know?
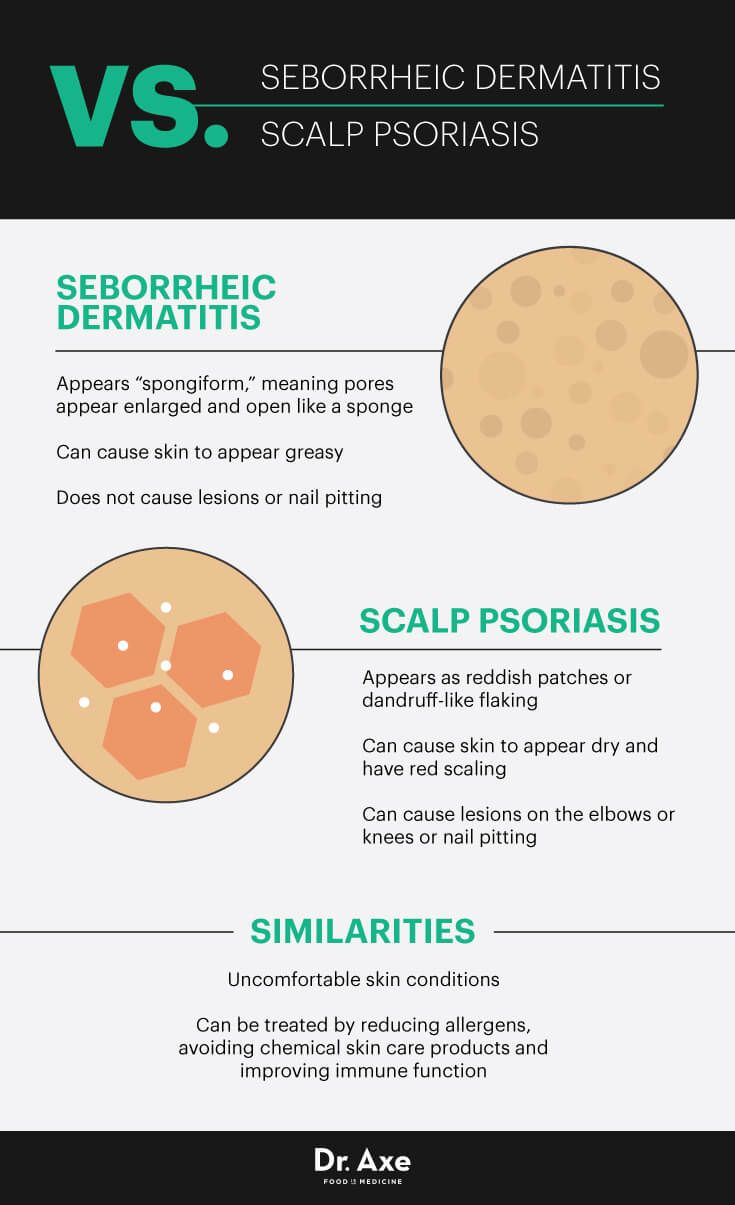
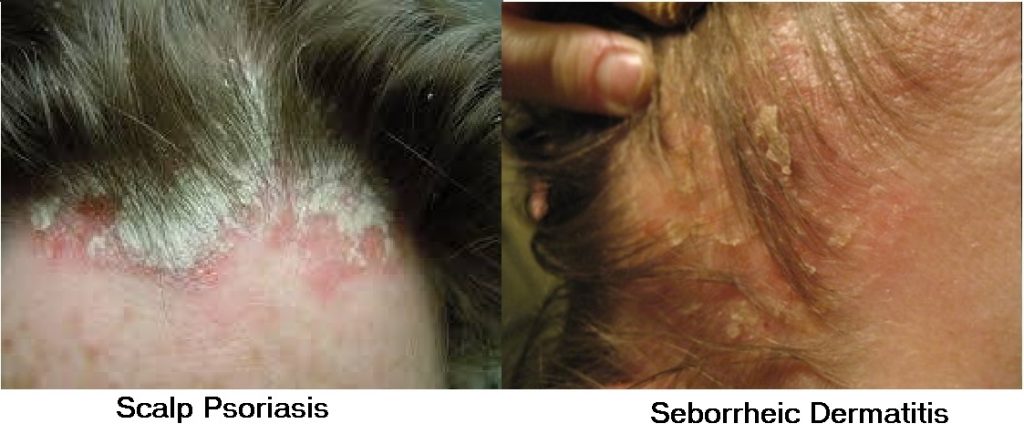
Symptoms may include fine scaling that looks like dandruff, or appear as thick, crusted plaques that cover the entire scalp. Other skin disorders, such as seborrheic dermatitis, may resemble psoriasis. However, scalp psoriasis appears powdery with a silvery sheen, while seborrheic dermatitis looks yellowish and greasy. Scalp psoriasis is common in patients of color, but treating it can be particularly tough due to the hair type.
Scalp psoriasis may be an indicator of psoriatic arthritis , as many people have both. If you think you have scalp psoriasis, see a dermatologist to diagnose scalp psoriasis and visit a rheumatologist to screen for psoriatic arthritis.
No matter how severe your scalp psoriasis is, there are options for treating the itching and flakes â from over-the-counter shampoos and topicals to light therapy, oral treatments and biologics.
Read Also: Home Remedies To Cure Psoriasis
How Is Sebopsoriasis Diagnosed
Sebopsoriasis is diagnosed by its clinical appearance following a detailed history and examination. A skin scraping for mycology may reveal Malassezia, but this is not diagnostic, as the yeast is a normal component of skin flora .
Skin biopsy is rarely performed in sebopsoriasis. It shows histopathological features intermediate between psoriasis and seborrhoeic dermatitis.
What Are The Symptoms Of Seborrheic Dermatitis
- Itchy white flakes of skin on your scalp . When scratched, the flakes come loose, mix in with your hair, or fall onto your neck and shoulders.
- Red scales on your skin.
- Crusty yellow scales on infants heads . Cradle cap shouldnt itch, but scratching may cause additional inflammation in the area and break the skin, leading to bleeding or mild infections.
- Blepharitis .
- Pinkish plaques of scales on both sides of your face.
- Flaky patches on your chest and at your hairline that are shaped like a flower petal or a ring.
- Redness in the folds and creases of your genitals, armpits and beneath your breasts.
- Inflamed hair follicles on your cheeks and the upper half of your trunk.
Also Check: Severe Psoriasis And Psoriatic Arthritis
How The Two Conditions Are Similar And Different
The similarities. Seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis tend to be lifelong conditions. They can take an emotional toll too, especially when the patches are very noticeable. Both can often be managed. Psoriasis usually needs stronger medicines than seborrheic dermatitis.
Both can also flare. This happens when youâre exposed to certain triggers that are unique to you, like the weather or stress.
Neither condition is contagious. You canât pass it to someone or get it from someone. But both conditions can run in families. So having one can be in your genes.
The differences. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease. That means your immune system is sending out faulty messages, and your body responds by growing skin cells too quickly.
Psoriasis plaques are itchy like seborrheic dermatitis, but they can also be painful. About one-third of people with psoriasis get a form of arthritis as the disease gets worse.
The scales on psoriasis plaques are thicker than those of seborrheic dermatitis, with more defined edges. Their color is closer to silver than the white or yellow of seborrheic dermatitis scales.
How To Tell Seborrheic Dermatitis From Psoriasis
To tell the two apart, youâll need to take a close look at the differences in those patches, or plaques. Psoriasis starts as rough, red, scaly skin and grows into thick, usually silver-colored scales on top of those areas. These patches often show up on the scalp. You can also get them on your torso, limbs, hands, and feet.
Seborrheic dermatitis patches are more likely to vary in color. They may look whitish-yellow, red, or brown. They also tend to feel greasy or oily . This form of dermatitis, or inflammation of the skin, strikes most often on the scalp, on oily parts of the face , and on the upper chest and back. Think of it as dandruff 2.0. Simple dandruff causes only flakes, no inflammation, and itâs only on the scalp.
Itâs tricky to figure out which condition is which when the flaky red patches are only on the scalp, with no other clues. Itâs also possible to have both conditions at the same time. Thatâs called sebopsoriasis, and it can leave you with white and silver flakes.
Also Check: Is It Bad To Pick Scalp Psoriasis
What Are Causes And Risk Factors Of Scalp Psoriasis
It is generally accepted that scalp psoriasis, like all psoriasis, is related to genetic defects that affect certain parts of the immune system. There are undoubtedly environmental risk factors that trigger its initial development in genetically predisposed individuals. The notion that “emotional stress” plays a causal role or at least exacerbates psoriasis has been difficult to prove. There is no question, however, that psoriasis of the scalp can be an extremely stressful experience.
What Medications Are Used To Treat Psoriasis And Eczema
There are many ways to treat psoriasis and eczema. In fact, some of the same treatments are used for both conditions.
Topical treatments
Topical treatments are ones that you apply directly to the skin, like creams, gels, and ointments. Some topical treatments are available over the counter, while others need a prescription.
Corticosteroids are the most common topical treatments for both psoriasis and eczema. They reduce inflammation, which helps with redness and itching. They come in different strengths, ranging from weaker to very strong .
Other topical medication options for psoriasis include:
-
Calcipotriene: helps to reduce inflammation, is chemically related to vitamin D, and is available in combination with a steroid in the medication betamethasone/calcipotriene
-
Calcitriol: helps to slow down skin cell growth and is also related to vitamin D
-
Tazarotene: helps to slow down skin cell growth and is chemically similar to vitamin A
-
Zithranol: helps to slow down skin cell growth and is available as a cream or shampoo
These are other topical medication options for eczema:
-
Tacrolimus andpimecrolimus: help reduce immune system activity, while not carrying the same risk of side effects that steroids have
-
Eucrisa: blocks a specific protein that causes inflammation in atopic dermatitis
Stronger treatments
People with more severe eczema and psoriasis may need stronger treatments that work throughout the body. These are usually given as an oral pill or shot.
Also Check: Can You Get Psoriasis Later In Life
Seborrheic Dermatitis Vs Psoriasis: Treatment
Since no definite causes have been found for either of the conditions yet, the treatment includes the alleviation of the symptoms and the possible avoidance of triggers.
- Topical treatments corticosteroids, vitamin D creams, anthralin, topical retinoids.
- treatment with natural and artificial ultraviolet light.
- Oral or injectable meds usually required for severe or persisting psoriasis. This treatment may have unpleasant side effects. Thats why its only used occasionally.
- Avoiding triggers patients keep a log of what they eat, drink, and do in order to identify the triggers to avoid them in the future.
- Different shampoos ketoconazole, salicylic acid, ciclopirox olamine
- Avoiding trigger mostly involves watching the diet.
As we can see, some of the treatment for both conditions are similar. However, the majority of approaches is different.
The main difference between seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis is that some seborrheic dermatitis may possibly be caused by fungus. Thats why for some patients, systematic use of ketoconazole may prevent dermatitis flare-ups.
However, even if the frequent use of ketoconazole may keep the symptoms at bay, it doesnt mean you have seborrheic dermatitis. You may still have psoriasis, which isnt appearing as often due to some other reasons.
Scalp Psoriasis Vs Seborrheic Dermatitis: Causes
Another thing psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis have in common is that their causes are unknown. For many years, scientists have been trying to figure out what causes these conditions in order to find the right preventive treatment. Unfortunately, they havent come up with anything so far.
There are theories that seborrheic dermatitis is caused by the yeast called Malassezia and/or an irregular response of the immune system.
When it comes to psoriasis, the only theory is currently an irregular immune system response. Scientists believe that T-cells, which normally defend the body against viruses and bacteria, start attacking healthy skin cells, thus causing the body to think it needs to heal a wound or fight an infection. Researchers cant figure out what misleads the T cells. Among the possible causes are genetics or environmental factors.
Overall, both psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis could be caused by the immune system overreaction.
Read Also: Que Es La Psoriasis Fotos
Seborrheic Dermatitis Vs Psoriasis Vs Eczema
When they see red patches with flakes, some people believe that they have eczema. If they are diagnosed with seborrheic dermatitis, its true. Seborrheic dermatitis is nothing more than one of the eczema types.
Most of the eczema types involve such symptoms as flaking, patching, itching, and burning. Each one of them requires a certain treatment approach.
How Is Seborrheic Dermatitis Treated
Treatment may depend on the severity of your condition. Everyone responds differently to medication, so it may take a few tries to find the right solution for you.
For some people, dandruff clears up on its own. Over-the-counter shampoos and medication are usually enough to improve flaking and soothe itching. If not, ask your doctor about prescription-strength products.
In babies, cradle cap doesnt always require treatment. It generally resolves well before the first birthday. In the meantime, use a mild baby shampoo. Massage the scalp gently using a very soft brush. Be gentle breaking the skin can lead to infection. If youre concerned about your babys scalp, see their pediatrician.
Also Check: Best Eye Cream For Psoriasis
The Differences Between Scalp Psoriasis And Seborrheic Dermatitis
How can I tell whether I have scalp psoriasis or seborrheic dermatitis? What symptoms do these two diseases share and how are they different? If you’ve been asking yourself these questions, you have come to the right place for answers. The purpose of this article is to outline the common characteristics of seborrheic dermatitis and scalp psoriasis as well as the key factors that make them different. We also touch upon some common remedies for these skin diseases, including nutritional therapy for scalp psoriasis and biotin for seborrheic dermatitis in infants.
Both psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis are common skin conditions. Scalp psoriasis is a subtype of psoriasis that occurs on the hair-covered areas of the head. As seborrheic dermatitis typically affects the scalp as well, it may be difficult to tell it apart from scalp psoriasis. The two disease also share similar symptoms including itchy, red, scaly skin which makes it even harder to distinguish between the two.
Causes Of Seborrheic Dermatitis
Similar to dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis is a harsh reaction to fungi that naturally lives on all humans. This is common in infants and referred to as a cradle cap. Whereas in adults, stress, hormonal changes, and dry weather can cause flare-ups. Diseases like Parkinsons, psoriasis and HIV can cause seborrheic dermatitis.
Also Check: Is Psoriasis A Serious Disease
Common Characteristics Of Patients
People who suffer from these two conditions come from all walks of life, but there may be some characteristics or clues that you are prone to one condition or the other. For example, while there is no known cause for psoriasis, it does appear that there may be a genetic link, as it tends to run in families.
Seborrheic Dermatitis is not necessarily shared through genetics, and anyone can potentially get it. However, it is typically found more in men than women. Although, there are several other potential causes.
- Family history
What Are Symptoms Of Scalp Psoriasis Vs Dandruff
Symptoms of scalp psoriasis and dandruff their similarities and differences are outlined in the table below.
| Symptoms of scalp psoriasis and dandruff that are similar | Additional symptoms of scalp psoriasis | Additional symptoms of dandruff |
|---|
- Certain medications
- Hormonal changes
- Certain illnesses such as Parkinsons disease and diseases that affect the immune system, such as HIV or AIDS
- Dandruff is not caused by allergies or poor hygiene.
Read Also: Why Does Psoriasis Flare Up
Scalp Psoriasis Vs Seborrheic Dermatitis
While both issues result in similar symptoms, they are not the same, and therefore need to be treated differently. For example, one is a disease, and the other is a condition. However, both problems can be alleviated with proper treatment and routine. To effectively treat the underlying problem, it is beneficial to understand how each is defined.
- Scalp PsoriasisScalp Psoriasis is a disease that results in a chronic condition of rapid skin growth. The skin cells grow too quickly for natural shedding, which leads to an accumulation of cells on the surface of the skin. Then, patches of scaly, rough skin appear on the scalp, causing itchiness and flaking. While psoriasis can appear anywhere on the body, this article is focused on the issue pertaining to the scalp.
- Seborrheic DermatitisSeborrheic Dermatitis is more commonly referred to as dandruff. It, too, causes a scaly and rough appearance on the scalp, resulting in itchiness and flaking. While similar to psoriasis, dermatitis does not appear to be as chronic or as invasive, meaning that cases of dandruff can be mild and temporary with a proper routine and treatment.
What Is Seborrheic Dermatitis

Seborrheic Dermatitis is almost like a hybrid dandruff. All dandruff is a result of a fungus that builds up on the scalp. Overtime, this fungus can grow and spread into what is known as seborrhoea. This seborrhoea can also grow on other oil-producing glands like the face or chest.
Unlike more normal forms of dandruff, seborrhoea can cause extreme itching, discomfort, redness and inflammation. It is usually characterized by an oily type of flake that falls off the scalp and spreads into hair.
Don’t Miss: Start Of Psoriasis On Scalp