What Does Plaque Psoriasis Look Like
About 80 to 90 percent of people with psoriasis have plaque psoriasis, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation. This makes it the most common type of psoriasis.
A plaque psoriasis rash looks like raised patches of thick, inflamed skin. On light skin, it looks red and scaly, often with a layer of silver on top. On skin with more pigment, the plaques look purple, gray, or darker brown and tend to be thicker.
Plaques can develop anywhere but are most likely to appear on your:
- scalp
- knees
- lower back
Plaques also tend to be symmetrical. For example, youre more likely to have plaques on both knees or elbows than on just one side. Other symptoms include:
- itching
2009 study of 1,593 people with psoriasis found that guttate psoriasis affects about 8 percent of people with psoriasis.
You can spot this type of psoriasis rash by small, raised round spots called papules. They sometimes have a scaly appearance. The spots might look red on light skin and purple or brown on skin with more pigment.
Guttate psoriasis can start at any age. For most people, though, it starts in childhood or adolescence. It can develop after an infection, such as strep throat or tonsillitis.
Its most likely to develop on the limbs and torso, though some people get it on the scalp, face, or ears.
Psoriasis can appear anywhere on the body. It can develop in just one area, or it can show up in several. For example, theres:
Plaque, inverse, and guttate are the most common types. Others include:
The Condition Of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune skin condition that causes many sufferers of the condition to hide their skin from the public eye.
Because of the obvious unattractive nature of psoriasis on the skin, many are embarrassed to show it and will try to avoid it being a topic of discussion.
This condition affects about 8 million people in the United States. It affects about 2 to 3 percent of people worldwide.
Its time to learn more about psoriasis.
What Injections Or Infusions Are Available For Psoriasis
Recently, a new group of drugs called biologics have become available to treat psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. They are produced by living cells cultures in an industrial setting. They are all proteins and therefore must be administered through the skin because they would otherwise be degraded during digestion. All biologics work by suppressing certain specific portions of the immune inflammatory response that are overactive in psoriasis. A convenient method of categorizing these drugs is on the basis of their site of action:
Drug choice can be complicated, and your physician will help in selecting the best option. In some patients, it may be possible to predict drug efficacy on the basis of a prospective patient’s genetics. It appears that the presence of the HLA-Cw6 gene is correlated with a beneficial response to ustekinumab.
Read Also: Coconut Oil To Treat Scalp Psoriasis
What Are The Symptoms Of Psoriasis
Psoriasis causes different symptoms in different people. Symptoms normally develop before age 45.
The most common symptoms are dry, raised, red patches of skin covered with silvery scales. The patches usually appear on the knees, elbow, lower back and scalp, but they can appear anywhere on the body.
Psoriasis can also cause dents and discolouration of the nails.
Some people get small, drop-shaped sores on the chest, arms, legs or scalp. Some people get swollen, painful joints.
The symptoms of some rare types of psoriasis include pus-filled blisters or a red, peeling rash that itches or burns intensely.
Cross section illustration of psoriasis
Close-up of psoriasis on skin
Types Of Psoriasis That Might Be Mistaken For Rosacea
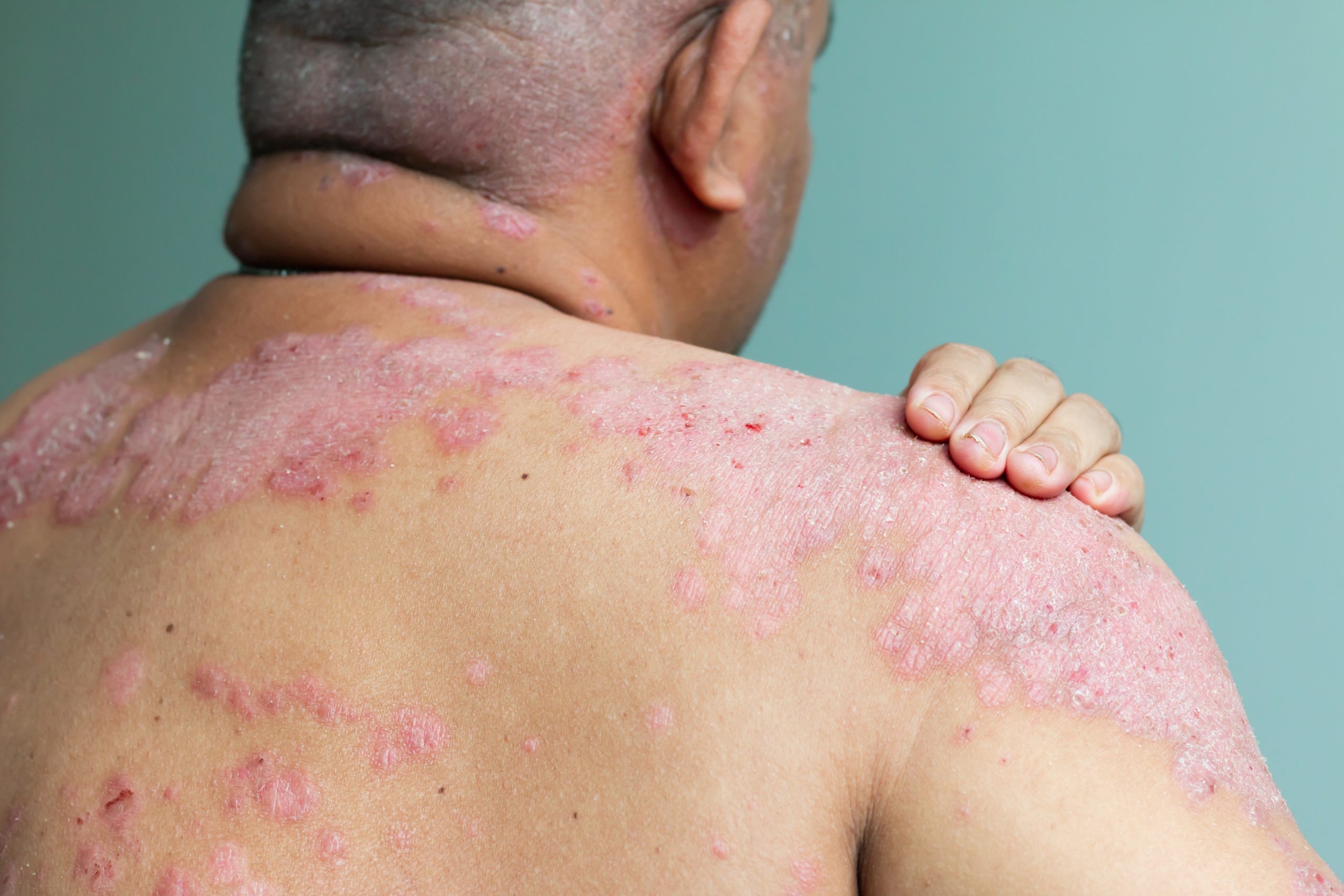
Generally, there are two kinds of psoriasis that might be mistaken for rosacea: plaque psoriasis and guttate psoriasis.
Plaque Psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis is the most common type of psoriasis by a wide margin, affecting up to 90 percent of people with the condition. The plaques seen in this type of psoriasis can vary in size and intensity. Some people may only have a few mild, coin-sized plaques, while others might see individual reddened plaques that connect and span to cover large patches of skin. Other symptoms of plaque psoriasis may include itching, stinging, burning, pain, or tightness.
Guttate Psoriasis
Like plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis can cause redness and itching. But, rather than appearing as hardened patches, this form of psoriasis presents as tiny bumps or teardrop-shaped lesions on the affected areas. Although symptoms most often appear on the torso, arms, and legs, guttate psoriasis can also affect the face, scalp, and ears.
You May Like: Why Do I Have Psoriasis On My Elbows
Seborrheic Dermatitis: Itchy Scaly Patches
A psoriasis skin rash tends to itch, burn, and feel sore. Patches of psoriasis commonly occur on your knees and elbows. Many people also have scalp psoriasis. The common skin rash seborrheic dermatitis also causes scaly, itchy skin patches. It can occur on your scalp, where it may be called dandruff, or on your face and chest. While doctors don’t know the exact cause of seborrhea, it occurs across the age spectrum, in babies as well as in adults, and is usually treated with creams and lotions.
What Type Of Psoriasis Treatment Will I Need
Several treatment options can relieve psoriasis. Creams or ointments may be enough to improve the rash in small areas of skin. If the rash affects larger areas, or you also have joint pain, you may need other treatments. Joint pain may be a sign that you have arthritis.
Your provider will decide on a treatment plan based on:
- Severity of the rash.
- Vitamin A or retinoid creams.
Also Check: Psoriasis On Face And Scalp
What Are The Types Of Psoriasis
In children, common types of psoriasis include:
Plaque psoriasis. This is the most common type of psoriasis. It causes plaques and silvery scales, usually on the knees, elbows, lower back, and scalp. They can be itchy and painful and may crack and bleed.
Guttate psoriasis. This type often shows up after an illness, especially strep throat. It causes small red spots, usually on the trunk, arms, and legs. Spots also can appear on the face, scalp, and ears.
Inverse psoriasis. This causes smooth, raw-looking patches of red skin that feel sore. The patches develop in places where skin touches skin, such as the armpits, buttocks, upper eyelids, groin and genitals, or under a woman’s breasts.
Diagnosis And Treatments For Psoriasis And Rosacea
The type of treatment you receive will depend on whether you are diagnosed with psoriasis or rosacea.
There is no specific test used to diagnose rosacea. Rather, a doctor will use your signs and symptoms, as well as a skin exam, to determine whether you have the condition. The doctor may order testing if they suspect that another condition, such as psoriasis, may be behind your symptoms. A skin biopsy is not usually performed, but blood work may be ordered to rule out autoimmune disease.
Psoriasis may be diagnosed using skin, scalp, and nail examinations. A doctor may also perform a biopsy to rule out other conditions and determine the type of psoriasis you have.
Also Check: Is Argan Oil Good For Psoriasis
What Are Psoriasis Triggers
Its important to understand your specific psoriasis triggers, Dr. Wassef says. Despite a great treatment plan, if you are still getting exposed to your psoriasis triggers, you will still flare, she notes. Finding and eliminating your triggers can help decrease the amount of medicine you use and limit the number of flares you have.
You may need to do some detective work to figure out your triggers, but keeping a journal that documents your symptoms, the timing of your flare, the weather conditions, your diet, and stress levels may help you pinpoint specific triggers if you have any. Not everybody with psoriasis can link their flares to certain triggers, Dr. Agbai says. In those individuals, genetic predisposition is thought to be the primary cause.
Psoriasis triggers include1:
- Living in cold, dry climates
- Having skin injuries, like a cut, scrape, or sunburn
- Experiencing stress
- Smoking or chronically being exposed to secondhand smoke
- Suddenly discontinuing an oral or systemic corticosteroids
What Are The Clinical Features Of Facial Psoriasis
Facial psoriasis has various clinical presentations. There are three main subtypes:
- Hairline psoriasis
- An extension of scalp psoriasis beyond the hairline onto facial skin
- Bright red, thickened plaques with variable white scale
Psoriasis affecting hairline
- Patchy involvement of the hairline
- Often affects the eyelids, eyebrows, nasolabial folds and beard area
- Salmon-pink, thin plaques with bran-like scale
- Usually associated with diffuse or patchy scalp psoriasis
- Psoriasis may or may not be present at other sites
Sebopsoriasis
- Sharply demarcated, red, scaly plaques
- May affect any part of the face
- Plaques tend to be symmetrical
- Associated with psoriasis at other sites including ears, genitals, scalp, elbows, knees, and trunk
- Soreness and skin sensitivity, which are usually mild
You May Like: Cual Es El Mejor Tratamiento Para La Psoriasis
Healthy Eating And Exercise
People with psoriasis have a slightly higher risk of developing diabetes and cardiovascular disease than the general population, although it’s not known why. Regular exercise and a healthy diet are recommended for everyone, not just people with psoriasis, because they can help to prevent many health problems.
Eating a healthy, balanced diet and exercising regularly can also relieve stress, which may improve your psoriasis.
Causes And Risk Factors Of Psoriasis
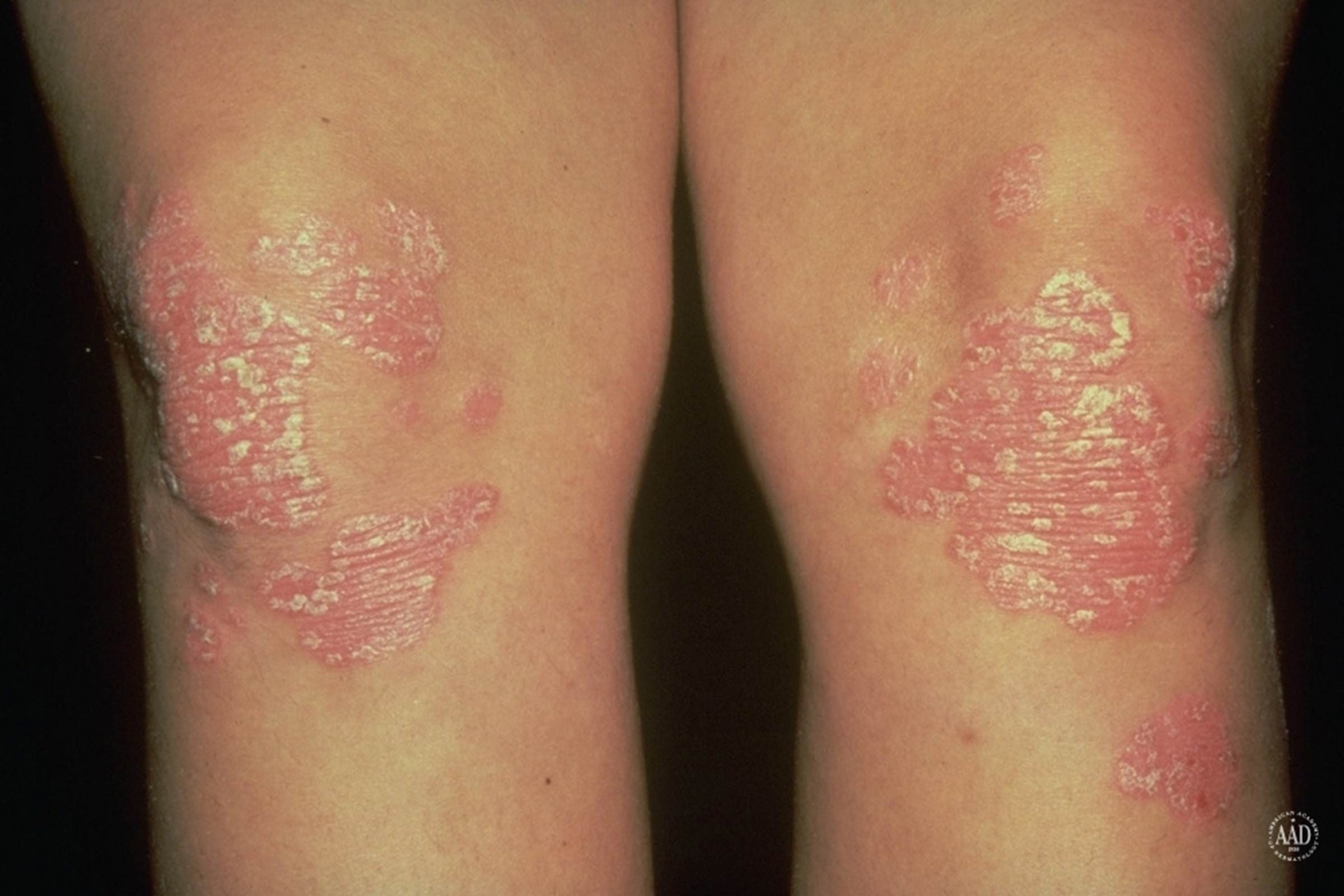
Psoriasis, in general, is a genetic condition passed down through families. “It’s likely that multiple genes need to be affected to allow psoriasis to occur and that it’s frequently triggered by an external event, such as an infection,” says James W. Swan, MD, professor of dermatology at the Loyola University Stritch School of Medicine in Maywood, Illinois.
Certain risk factors, such as a family history or being obese, may increase your odds of developing psoriasis.
According to the National Psoriasis Foundation , at least 10 percent of people inherit genes that could lead to psoriasis, but only 3 percent or less actually develop the disease. For this reason, it is believed that the disease is caused by a combination of genetics and external factors or triggers.
A psoriasis outbreak may be provoked by:
Don’t Miss: Cerave Psoriasis Moisturizing Cream Walgreens
What Is Facial Psoriasis
Facial psoriasis is a chronic skin condition in which there are one or more, persistent, thickened, red and dry patches on the face.
Psoriasis is a common chronic inflammatory skin disease that may affect any skin site. Facial involvement occurs at some time in about half those affected by psoriasis. Although it is usually mild, facial psoriasis is occasionally very extensive involving the hairline, forehead, neck, ears and facial skin.
It is extremely rare to have psoriasis occurring solely on the face. Most patients also have scalp psoriasis and they may also have moderate to severe psoriasis at other sites.
Patients with facial psoriasis often suffer from psychosocial problems due to the presence of unsightly red, scalyplaques on highly visible areas.
Facial involvement presents as a therapeutic challenge because facial skin is thin, sensitive and more complicated to treat.
What Is Plaque Psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis is a skin condition that can appear as raised plaques and scales. It looks pink or silvery on lighter skin and purple or yellowish on darker skin, says Dr. Friedman.
The condition is associated with inflammation caused by immune system dysfunction, says the NPF. In other words, a person’s immune system overreacts to some genetic or environmental trigger, causing the inflamed, scaly patches we know as plaque psoriasis to appear.
Symptoms of psoriasis often begin between 15 and 25 years old, notes the NPF. However, people of any age can develop the condition.
You May Like: Best Over The Counter Shampoo For Psoriasis
Eczema: Red Itchy Irritated Skin
Like psoriasis, eczema is a chronic skin condition that often causes intense itching. Scratching causes redness and inflammation of the skin, leading to a worsening of the eczema. Scratching can also cause a secondary bacterial infection. The most common type of eczema is caused by a reaction to irritants like detergents, soaps, or household cleansers. So if you have eczema, you should be careful to use mild soap and regularly moisturize your sensitive skin. Your doctor may prescribe a steroid cream or other medications if eczema is severe.
What Is Psoriasis And What Causes It
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition. If you have psoriasis, it means your skin cells regenerate much faster than usual, causing them to build up. Anyone can get psoriasis, but its not contagious.
There are several types of psoriasis and, like other autoimmune diseases, they may involve flare-ups and periods of remission. You can even have more than one type.
Some common triggers for psoriasis are:
- certain medications
Read Also: Castor Oil For Psoriasis On Scalp
Psoralen Plus Ultraviolet A
For this treatment, you’ll first be given a tablet containing compounds called psoralens, or psoralen may be applied directly to the skin. This makes your skin more sensitive to light. Your skin is then exposed to a wavelength of light called ultraviolet A . This light penetrates your skin more deeply than ultraviolet B light.
This treatment may be used if you have severe psoriasis that hasn’t responded to other treatment. Side effects of the treatment include nausea, headaches, burning and itchiness. You may need to wear special glasses for 24 hours after taking the tablet to prevent the development of cataracts. Long-term use of this treatment isn’t encouraged, as it can increase your risk of developing skin cancer.
Are There Alternative Therapies For Psoriasis
Conventional therapy is one that has been tested with clinical trials or has other evidence of clinical effectiveness. The FDA has approved several drugs for the treatment of psoriasis as described above. Some patients look to alternative therapy, diet changes, supplements, or stress-reducing techniques to help reduce symptoms. For the most part, alternative therapies have not been tested with clinical trials, and the FDA has not approved dietary supplements for treatment of psoriasis. There are no specific foods to eat or to avoid for patients with psoriasis. However, some other therapies can be found on the National Psoriasis Foundation web site. Individuals should check with their doctors before starting any therapy.
Read Also: Best Moisturizer For Scalp Psoriasis
Some Symptoms Associated Psoriatic Arthritis
Symptoms can vary greatly from patient to patient. Let your doctor know if you have the following symptoms which may indicate psoriatic arthritis:
- Joint pain especially with redness, swelling and tenderness.
- Dactylitis inflammation of an entire digit, either a finger or toe which swells up to a sausage shape and can be painful.
- Nail changes loosened, thickened or pitted nails .
It has been suggested that the presence of 20 nail pits distinguishes patients with PsA from those with rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis.
- Morning stiffness/pain in the back that improves with movement.
- Pain in your heel or tennis elbow.
And There Are Ways To Prevent Flare
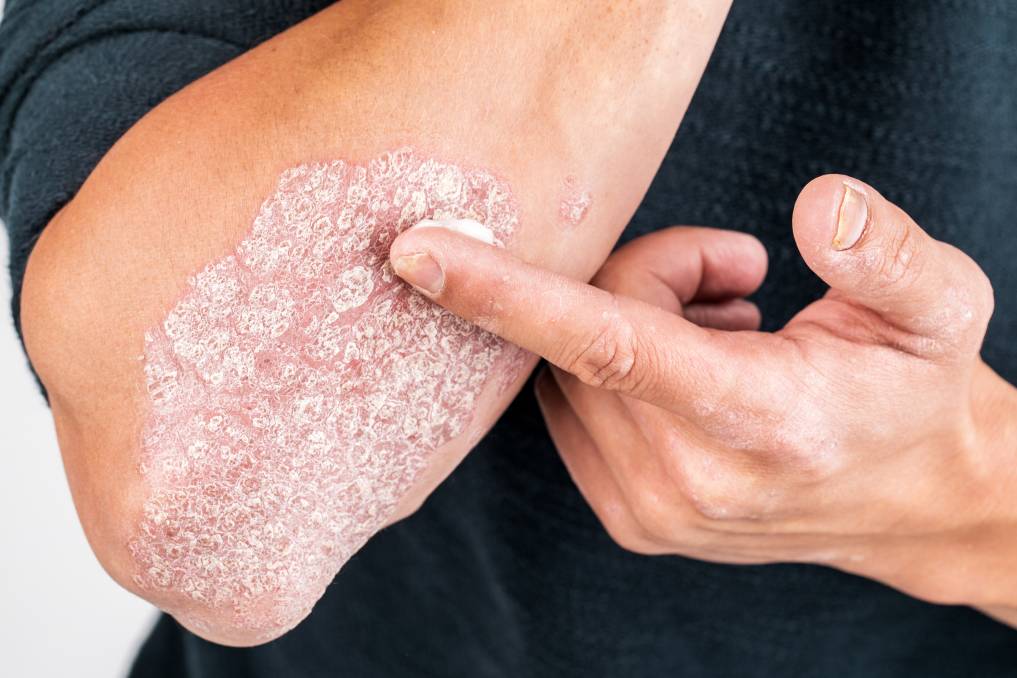
Medicines work best, but you can do things to treat your psoriasis without a prescription. Here are some things you can do at home to help with psoriasis flare-ups.
Before you go to bed, wrap your skin with a bandage or plastic wrap. In the morning, wash the area gently. Over time, this can help with scaling.
Take shorter showers as water can strip your skin of natural oils. Also, make sure the water is not too hot as hot water can dry out the skin. Right after your bath or shower, pat your skin dry with your towel, and immediately apply a high-quality body cream to seal in the moisture. Ask a dermatologist to recommend a suitable product. If your doctor prescribes creams or ointments, be sure to use them as instructed.
Smoking and alcohol use can trigger psoriasis flare-ups so its a good idea to quick smoking for good, and cut back on drinking. Kicking the habit is one of the best things you can do for your skin.
High-stress levels can also trigger a flare-up. Exercise, do yoga and/or mediation to help you manage your stress levels. Also be sure youre eating a balanced, healthy diet, and avoid foods that may trigger a flare-up as well.
Also Check: What Shampoo Can I Use For Psoriasis
What Psoriasis Medications Can I Take
Systemic Medications
Biologics for Psoriasis
The following drugs are categorized under the term biologic because they are all proteins produced in the laboratory by industrial cell culture techniques and must be given either subcutaneously or intravenously. The frequency of treatment depends on the specific drug. All of these medications are very precise in that they block only one or two parts of the inflammatory reaction and are moderately immunosuppresive.
Biologics are expensive and do not cure psoriasis but as a group are quite effective and reasonably safe. If it is decided to start a patient on a biologic drug, the choice will depend on the particular physician’s expertise, as well as insurance coverage and payment issues.
Psoriasis Can Cause Arthritis
For an unknown reason, psoriasis can cause a form of arthritis known as psoriatic arthritis. Symptoms include:
- discomfort, throbbing or swelling in one or many joints
- tenderness in any joint
- pain caused by inflammation in the joints, which stimulates nerve endings.
- The joints most likely to be affected are the last joint in the fingers or toes, the sacrum , wrists, knees or ankles.
Don’t Miss: Does Sweating Make Psoriasis Worse
Is Psoriasis Contagious
No, psoriasis is not contagious. People used to believe that psoriasis was the same as leprosy, but that is not the case. You cannot get psoriasis by touching, kissing, or having sex with someone who has psoriasis. People get psoriasis because of their genes, not their hygiene, diet, lifestyle, or any other habits.