Shingles: A Rash And Severe Pain That Lingers
Shingles is another viral infection that shares some symptoms with psoriasis. Like psoriasis, shingles can make your skin burn and itch and produces a red, blistered skin rash. Shingles is caused by the same virus that first brings on chickenpox. The virus stays in your body and can come back years later to cause shingles, especially during times of stress or infection. The skin rash of shingles follows the course of a single nerve, usually on the trunk. In some cases, severe pain lasts long after the burning, itchy rash disappears. Shingles is more common in people over age 50.
How Long Does Pityriasis Rosea Last
Pityriasis rosea clears up in about six to twelve weeks. Pale marks or brown discolouration may persist for a few months in darker-skinned people but eventually, the skin returns to its normal appearance.
Second attacks of pityriasis rosea are uncommon , but another viral infection may trigger recurrence years later.
What Are Treatment Options For Pityriasis Rosea How Long Does Pityriasis Rosea Last
- The prognosis for pityriasis rosea is excellent as the rash is self-limiting and usually clears even without treatment within nine weeks.
- It typically leaves no long-lasting scars, although some mild, temporary skin discoloration called post inflammatory hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation can occur in people with darker skin.
- It has no known long-lasting side effects and has not been associated with any other diseases.
- Symptoms may be reduced with topical treatment or taking extra precautions to prevent overheating.
- Once a person has pityriasis rosea, they generally have lifelong immunity.
Also Check: Does Guttate Psoriasis Go Away
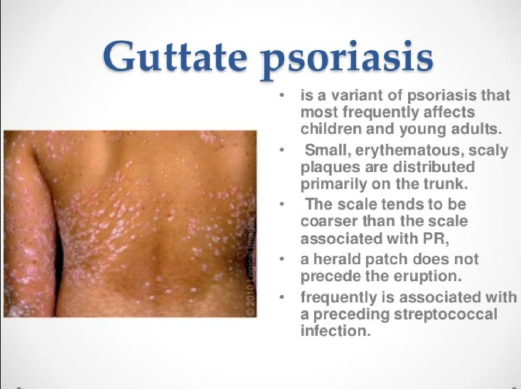
Who Gets Guttate Psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis tends to affect children and young adults it is the second most common form of psoriasis in children after chronicplaque psoriasis. Both sexes and all races can develop guttate psoriasis. It is often the first presentation of psoriasis for an individual, but can also be seen in those with known chronic psoriasis.
Acne: Blocked Pores That Lead To Pimples
Some forms of psoriasis appear as pus-filled blisters that may be confused with pimples. Pustular psoriasis forms white blisters that are filled with pus and surrounded by red skin. Far more common than psoriasis, acne also causes a pus-filled pimple eruption. However unlike psoriasis acne is caused by excess oil, blocked pores, and bacteria. Acne is common in teens and young adults and occurs on the face, neck, back, or chest. Pustular psoriasis is usually seen in adults and can occur anywhere on the body, but less likely on the face.
Don’t Miss: First Line Treatment For Psoriasis
What’s The Outlook Like After Having Guttate Psoriasis
- In nearly two thirds of people the spots clear up and never come back.
- Occasionally the spots turn into a more long-term type of psoriasis called plaque psoriasis. This can be treated with similar creams and light treatment.
- Once it’s cleared, sometimes a second outbreak of guttate psoriasis happens. This could happen if the streptococcus bug is lurking in your tonsils.
- Thankfully the guttate psoriasis never properly scars, although sometimes it can leave tiny pale marks where it used to be: these should fade with time though.
Risks For Tinea Versicolor
Doctors are also unsure about why some people get tinea versicolor, and others do not. However, some general risk factors make it more likely. These include:
- living in a hot, humid climate
- sweating a lot
- having oily skin
- having a weakened immune system
A dermatologist can usually diagnose tinea versicolor by looking at a persons skin. If they are unclear on the diagnosis, they may scrape off a bit of skin to examine under a microscope. Alternatively, they might examine the skin using a Wood lamp, which is a diagnostic tool that emits a specific type of light. A doctor can make a diagnosis if the affected skin appears yellowish-green when looked at it under the lamp.
Although psoriasis and tinea versicolor have similar symptoms, the underlying causes and treatment options are very different.
You May Like: Causes Of Psoriasis And Eczema
What Causes Pityriasis Rosea
Pityriasis rosea is associated with reactivation of herpesviruses 6 and 7, which cause the primary rash roseola in infants. Influenza viruses and vaccines have triggered pityriasis rosea in some cases.
Pityriasis rosea or atypical, pityriasis rosea-like rashes can rarely arise as an adverse reaction to a medicine. Reactivation of herpes 6/7 is reported in some but not all cases of drug-induced pityriasis rosea. Pityriasis rosea-like drug eruptions have been caused by angiotensin-converting enzymeinhibitors, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hydrochlorothiazide, imatinib, clozapine, metronidazole, terbinafine, gold and atypical antipsychotics.
What Is Pityriasis Rosea What Is Psoriasis
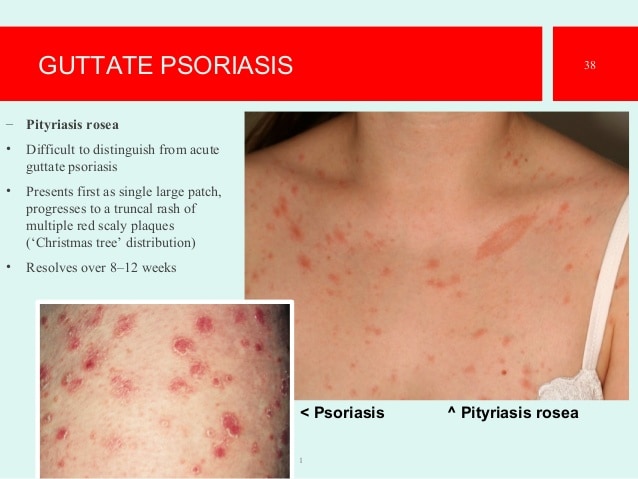
As autumn approaches, our providers at Advanced Dermatology expect to see a predictable shift in the types of skin issues that they diagnose and treat. Many skin conditions tend to follow a seasonal pattern. For example, pityriasis rosea is a peculiar skin rash that is very common in the fall and spring seasons. Usually it begins as a large pink or red patch with a scaly border. This typically appears on the torso and it may be confused with eczema or ringworm, even by the well-trained eye. Within several days, the rash progresses to include between a few and many dozen smaller, oval, scaly, pink patches, which may or may not itch. These primarily occur on the torso, upper arms, and upper legs. Classically, the patches on the back resemble a Christmas tree pattern, with a downward-slanting orientation of the outermost patches.
Although usually quite concerning to patients, the good news is that PR has no medical significance. Without treatment it usually lasts about 6-12 weeks, and it leaves no permanent marks or scars on the skin. The official cause is unknown, but it is suspected that PR may be due to a yet-unidentified virus. This is because in some people, the rash occurs following a mild illness, and once a person has had PR, the rash does not typically ever recur. Finally, cases of PR tend to cluster, similar to what one would expect with viral illness.
You May Like: Is Psoriasis Caused By Inflammation
What Is The Cause Of The Disease
-
Etiology
-
Pathophysiology
The pathogenesis of pityriasis rosea is poorly understood. However, given the nature of the disease to occur in outbreaks and its low rate of reoccurrence, it is believed there is an infectious agent responsible for the disease that has not been identified. To date, evidence suggests that human herpes virus 6 or Human Herpes Virus 7 may possibly play a role in its pathogenesis however, this is still controversial. The skin lesions may represent a reactive response of systemic viral replication in contrast to direct inoculation. Again, there is no evidence to date to support these claims.
Several medications have been reported to cause a pityriasis rosea-like reaction including:
-
anti-hypertensives: captopril, clonidine, hydrochlorothiazide, atenolol
-
antipsychotics: asenapine, clozapine, nortriptyline, barbiturates, bupropion
-
biological agents: adalimumab, rituximab
-
antibiotic/antifungals: metronidazole, pristinamycin, terbinafine
-
metals: arsenic, bismuth, gold
-
other: isotretinoin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, omiprazole, D-penicillamine, levamisole, pyribenzamine, ergotamine tartrate, pristinamycin, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Pityriasis rosea-like eruptions have been described after several vaccines including: diphtheria, smallpox, pneumococcal, hepatitis B, H1N1 influenza, yellow fever, smallpox, humanpapillomavirus, and bacillus Calmette-Guérin .
What Causes Guttate Psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis typically develops 12 weeks after a streptococcal infection of the upper respiratory tract, particularly tonsillitis, or other sites such as perianal streptococcal dermatitis. Beta-haemolytic streptococci can directly stimulate skin-homing T-cellproliferation in the tonsils.
Guttate psoriasis has been reported to follow SARS-CoV-2 infection and other viral infections such as coxsackievirus.
You May Like: Does Guttate Psoriasis Leave Scars
How Is Guttate Psoriasis Diagnosed
There aren’t any particular tests for guttate psoriasis.
It’s diagnosed by the way it looks and also by finding out if there has been a throat infection a few weeks before. Occasionally a blood test can be used to detect the streptococcus germ : this is called an anti-streptolysin antibody assay.
A biopsy of the skin is not usually needed. If it isn’t quite clear what the skin condition is, a specialist skin doctor might use a small microscope to look at it more closely.
Dry Cracked Skin: Irritation That Can Lead To Infection
Dry, cracked skin is a psoriasis symptom. However, dry air can also cause your skin to become dry and itchy. When the skin is dry and irritated , it’s more likely to get infected. Infection may cause your skin to become red and swollen. If you have any skin rashes that keep coming back or won’t go away, see your doctor. Most cases of psoriasis can be diagnosed with a physical examination but because psoriasis can look like many other skin conditions, a skin biopsy may have to be done to definitively diagnose it.
You May Like: What Happens If You Pick Psoriasis
Dermoscopy Differentiates Guttate Psoriasis From A Mimickerpityriasis Rosea
2021 Vol 11, No 1 | January
| Department of Dermatology, HBT Medical College & Dr. R.N. Cooper Hospital, Mumbai, India | |
| Tishya Singh | Department of Dermatology, HBT Medical College & Dr. R.N. Cooper Hospital, Mumbai, India |
| Yasmeen Khatib |
Citation: Makhecha M, Singh T, Khatib Y. Dermoscopy differentiates guttate psoriasis from a mimickerpityriasis rosea. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2021 11:e2021138. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5826/dpc.1101a138
Accepted: August 31, 2020 January 29, 2021
Copyright: ©2021 Makhecha et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License BY-NC-4.0, which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Funding: None.
Competing interests: The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
All authors have contributed significantly to this publication.
Corresponding author: Tishya Singh, MBBS, DNB, Department of Dermatology, Chaudhary Hospital, Mohali, India. Email: tishyasingh@gmail.com
Eczema: Red Itchy Irritated Skin
Like psoriasis, eczema is a chronic skin condition that often causes intense itching. Scratching causes redness and inflammation of the skin, leading to a worsening of the eczema. Scratching can also cause a secondary bacterial infection. The most common type of eczema is caused by a reaction to irritants like detergents, soaps, or household cleansers. So if you have eczema, you should be careful to use mild soap and regularly moisturize your sensitive skin. Your doctor may prescribe a steroid cream or other medications if eczema is severe.
Read Also: Selsun Blue Shampoo For Psoriasis
Seborrheic Dermatitis: Itchy Scaly Patches
A psoriasis skin rash tends to itch, burn, and feel sore. Patches of psoriasis commonly occur on your knees and elbows. Many people also have scalp psoriasis. The common skin rash seborrheic dermatitis also causes scaly, itchy skin patches. It can occur on your scalp, where it may be called dandruff, or on your face and chest. While doctors don’t know the exact cause of seborrhea, it occurs across the age spectrum, in babies as well as in adults, and is usually treated with creams and lotions.
What Happens After The First Outbreak
Usually it comes and goes and then that’s all there is to it. In about 80% of people the spots will fade in three weeks to three months and never come back. But in some people it carries on to be long-term plaque psoriasis. Sometimes you can get a second outbreak, particularly if the streptococcus germ is still in your throat or tonsils.
Read Also: How To Loosen Psoriasis Scales On Scalp
How Psoriasis Is Diagnosed
A GP can often diagnose psoriasis based on the appearance of your skin.
In rare cases, a small sample of skin called a biopsy will be sent to the laboratory for examination under a microscope.
This determines the exact type of psoriasis and rules out other skin disorders, such as seborrhoeic dermatitis, lichen planus, lichen simplex and pityriasis rosea.
You may be referred to a specialist in diagnosing and treating skin conditions if your doctor is uncertain about your diagnosis, or if your condition is severe.
If your doctor suspects you have psoriatic arthritis, which is sometimes a complication of psoriasis, you may be referred to a doctor who specialises in arthritis .
You may have blood tests to rule out other conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, and X-rays of the affected joints may be taken.
Who Is Affected By Guttate Psoriasis
- Usually young people get guttate psoriasis, in their teens or twenties. Men and women are affected equally.
- It seems to occur all over the world.
- No one really quite knows how common it is. In general, a GP in the UK would have heard of it and probably know how to diagnose it, but they may not have seen a case themselves for many years.
Also Check: What Is The Reason For Psoriasis
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Tinea versicolor is a relatively common skin disorder that may be encountered by the nurse practitioner, internist, dermtologist and primary care physician. The diagnosis is usually made on clinical features but does require clinical acumen. The rash is benign and may spontaneously disappear.
Patients should be informed that the causative agent of pityriasis versicolor is a commensal fungal inhabitant of the normal skin flora, and therefore the disease is not considered to be contagious. In addition, pityriasis versicolor does not lead to either permanent scarring or pigmentary disorders. However, in many cases, disease recurrence may occur despite effective treatment. An interprofessional team of a nurse and clinician should provide patient education which will decrease their anxiety and provide the best patient outcome.
The outcomes in most patients are excellent.
How To Recognize Pityriasis Rosea
Pityriasis rosea is a common, sometimes itchy rash that resolves on its own. The rash begins with a herald patch and continues to spread in a characteristic pattern, typically over the course of six to eight weeks.
The cause of pityriasis rosea is unknown and there is no cure to date. These photos illustrate the phases and characteristics of pityriasis rosea.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
James Heilman, MD / Wikimedia Commons / CC BY-SA 3.0
Pityriasis rosea is a common, itchy rash that resolves on its own. The rash begins with a herald patch, pictured here. The herald patch is a single 2 to 10 centimeter round or oval-shaped lesion that most often appears on the trunk and resembles ringworm.
Within a few days, smaller lesions appear mainly on the trunk or wherever the herald patch is located, but they can also spread to the arms, legs, and face. Lesions can continue to spread several weeks after the herald patch first appeared.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
Joe Miller
This is another example of a herald patch at the onset of pityriasis rosea. A full rash usually develops within a few days or several weeks of the herald patch’s appearance. Pityriasis rosea typically occurs in people between 10 and 35 years of age.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
Joe Miller
Joe Miller
You May Like: Mild To Severe Plaque Psoriasis
Ringworm: Fungal Infections Of The Skin And Nails
Tinea is a type of fungal infection that resembles some symptoms of psoriasis. Psoriasis can cause the thick fingernails symptomatic of fungal nail infections, and both can cause red, itchy skin rashes. When tinea grows on your skin, it can cause a scaly, red skin rash that clears in the middle, called ringworm . Fungal infections of the skin and nails can be hard to treat. Antifungal medications work, but you may need to take them for a long time.
Heat Rash: Sweating That Leads To Bumpy Red Skin
Inverse psoriasis is a type of psoriasis that forms in the armpits and skin folds under breasts or in groin areas, making the skin red and shiny. Sweating makes this type of psoriasis worse. Heat rash also makes your skin red and forms in skin folds of the groin, breasts, and armpits. Heat rash occurs in hot, humid conditions. Sweating can cause your pores to get blocked and result in a bumpy, red skin rash that stings. Heat rash is more common in newborns, but can also affect older children and adults.
Recommended Reading: At What Age Can You Get Psoriasis
Guttate Psoriasis: Small Red Spots
Guttate psoriasis the second most common type of psoriasis is characterized by multiple small, round red spots on the skin, usually widespread across the trunk and limbs. Often resulting from a bacterial or viral infection in children, such as strep throat, these spots come on suddenly and sometimes require oral medication or injections. Mild cases, however, may clear up without treatment.
What Are Some Common Misdiagnoses Of Pityriasis Rosea
The first herald patch of pityriasis rosea may look very similar in appearance to ringworm . Pityriasis rosea has also been mistaken with eczema and psoriasis, which can occur as similar scaly patches, but not in the same distribution as pityriasis rosea.
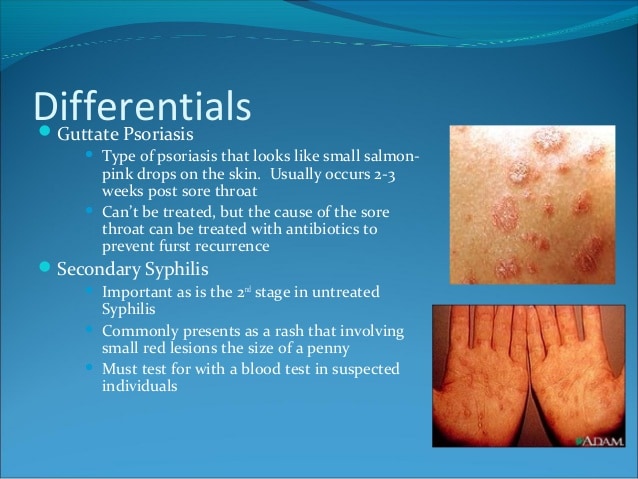
Pityriasis rosea may be misdiagnosed as psoriasis, eczema, fungal infection , secondary syphilis, drug eruption , fixed drug eruption , pityriasis lichenoides chronica, parapsoriasis, or lichen planus.
Don’t Miss: Over The Counter Psoriasis Cream
How Is Pityriasis Rosea Diagnosed
The diagnosis of pityriasis rosea is usually made clinically but may be supported by the finding of subacute dermatitis on histopathology of a skin biopsy. Eosinophils are typical of drug-induced pityriasis rosea. Blood testing for HHV6 is not indicated because nearly 100% of individuals have been infected with the virus in childhood and existing commercial tests do not measure HHV6 activity.
Fungal scrapings are sometimes sent for mycology to exclude fungal infection .
| Essential clinical features |
|---|
|
| Optional clinical features |
At least one of the following features should be present:
|