Potential Drug Involvement In Psoriasis
In clinical practice, identifying drug-related causes of a psoriasis flare can be difficult for various reasons. One complicating factor is that the latency period between start of the medication and onset of psoriatic skin lesions can vary considerably between drugs. Medications with a typically short latency period include terbinafine, whereas lithium and beta-blockers can be associated with relatively long latency periods up to 12 months. Consequently, a temporal relationship is sometimes not immediate apparent. A psoriasis flare in the absence of known triggering factors such as infection and emotional stress should raise the possibility of a drug-related cause. Another issue is that the psoriasis flare can persist following discontinuation of the suspected medication. Moreover, there may be little difference between classical psoriasis and drug-related psoriasis in terms of clinical and histopathological features.
A tool to help to better discern potential causal drug relations is the Naranjo adverse drug reaction probability scale., The scale consists of 10 questions, the scoring of which results into four categories: definite, probable, possible, and doubtful . Assessment with the Naranjo scale could be helpful for clinical practice to strengthen a possible drug association.
Psoriasiform Drug Eruption Induced By Anti
Jae-Jeong Park1, Yoo Duk Choi2, Jee-Bum Lee1, Seong-Jin Kim1, Seung-Chul Lee1, Young Ho Won1 and Sook Jung Yun1*
Accepted November 23, 2009.
Psoriasiform drug eruptions can be induced by several drugs . Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by T-cell-mediated cytokine production that drives the hyperproliferation and abnormal differentiation of keratinocytes . Drugs can cause new lesions when there is no history or family history of psoriasis. Based on the psoriatic drug eruption probability score, -blockers, synthetic anti-malaria drugs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , lithium, digoxin, and tetracycline antibiotics are relevant in psoriasis .
Common cutaneous adverse effects of anti-tuberculosis medication include morbilliform rash, urticaria, lichenoid drug eruption, exfoliative dermatitis, hyperpigmentation, erythema multiforme-type drug eruption and Stevens-Johnson syndrome .
We report here the first case of a psoriasiform drug eruption in a man taking anti-tuberculosis medication.
CASE REPORT
Fig. 1. Widespread erythematous papulosquamous lesions on the trunk and buttocks, and both legs.
DISCUSSION
REFERENCES
Antimalarial Drugs: Chloroquine And Hydroxychloroquine
The synthetic antimalarial drugs chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine are associated with plaque type psoriasis exacerbations. There have been several descriptions of worsening of psoriasis in individuals receiving antimalarial prophylaxis., Furthermore, there have been cases reported of psoriasis exacerbation with the use of hydroxychloroquine as immunomodulating treatment for lichen planopilaris and psoriatic arthritis. Rarely, these antimalarial drugs are linked to induction of psoriasis. The latency period of psoriasis exacerbation is usually between 4 and 12 weeks. Morphological variants of -chloroquine-related psoriasis other than plaque type psoriasis include pustular psoriasis and erythroderma. The exact risk of psoriasis exacerbation or induction related to antimalarial drugs remains unknown.
Also Check: Foods To Avoid With Psoriasis Arthritis
Bitte Loggen Sie Sich Ein Um Zugang Zu Diesem Inhalt Zu Erhalten
Für Ihren Erfolg in Klinik und Praxis – Die beste Hilfe in Ihrem Arbeitsalltag
Mit e.Med Interdisziplinär erhalten Sie Zugang zu allen CME-Fortbildungen und Fachzeitschriften auf SpringerMedizin.de.
Sie können e.Med Interdisziplinär 14 Tage kostenlos testen . Der Test läuft automatisch und formlos aus. Es kann nur einmal getestet werden.
Clinical Features Of Drug
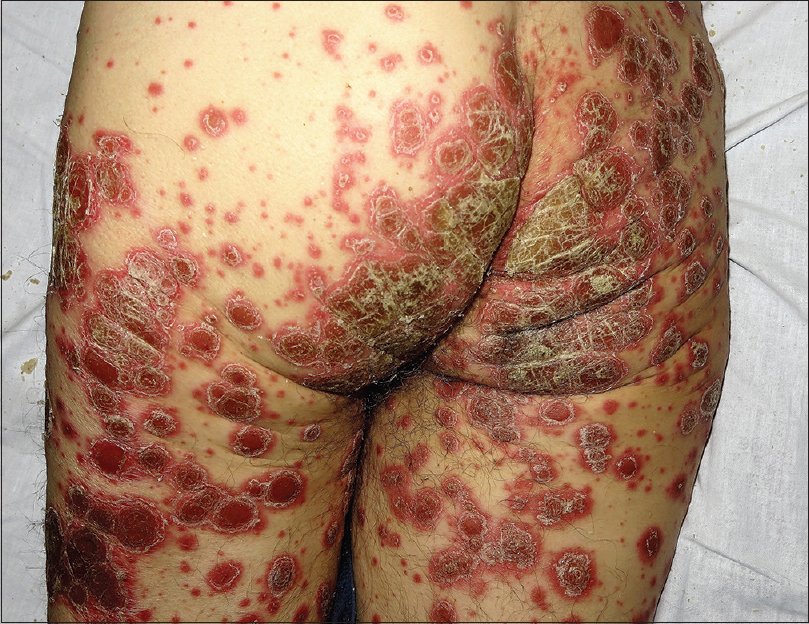
The clinical spectrum of drug-related psoriasis is as diverse as typical nondrug-related psoriasis itself. Morphological types that have been described as drug reaction included plaque psoriatic skin lesions, palmoplantar psoriasis, nail psoriasis, scalp psoriasis leading to alopecia, pustular psoriasis, and erythrodermic psoriasis. Furthermore, transformative drug-reactions have been described, eg, pustular psoriasis induction in a patient with a personal history of plaque psoriasis. There are no clear specific psoriasis phenotypes provoked by the different drugs implicated in drug-related psoriasis.
There are no clear clinical criteria to distinguish the morphology of drug-induced psoriasis to that of typical psoriasis. However, in some cases, so-called psoriasiform skin lesions are described. Clinically, such skin lesions are almost similar to classic psoriasis cases but lack certain characteristics of psoriasis. For instance, psoriasiform skin lesions may miss well-demarcated borders or lack the coarse scaling typical of psoriasis.
The severity of drug-related psoriasis can vary considerable. There have been documented cases of generalized psoriasis and erythrodermic psoriasis, requiring hospitalization for proper management.,
Read Also: How Do You Treat Psoriasis Naturally
Specific Drug Associations Linked To Psoriasis
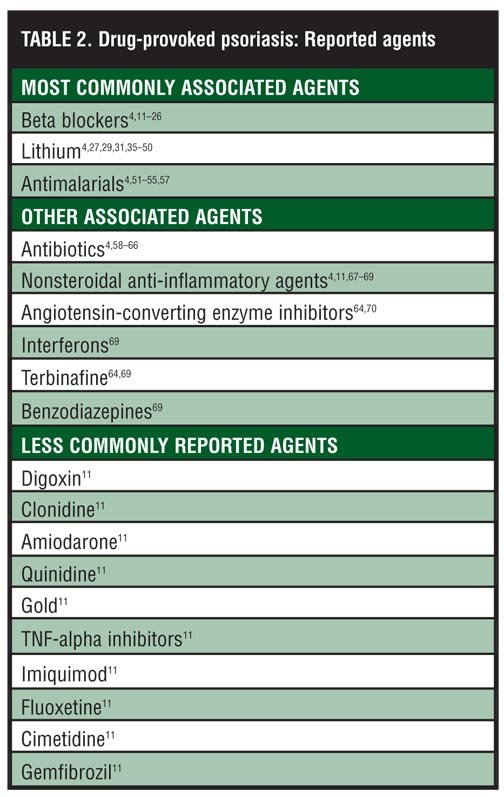
The list of drugs that have associations with drug-related psoriasis is quite extensive. For most drugs, however, the evidence is limited to anecdotal reports. Consequently, there are often insufficient grounds to clearly define the risk of a particular drug in context of its psoriasis induction of exacerbation potential. Traditionally, there have been strong associations documented for beta-blockers, lithium, synthetic antimalarial drugs, interferons, imiquimod, and terbinafine . Of note, most of these associations stem from the 1970s and 1980s, in particular for lithium and synthetic antimalarial drugs.
Management Of The Ibd Following Withdrawal Of Tnf
In the studies,,,,,,,,,, describing IBD development after discontinuation of TNF- antagonists, gastrointestinal symptoms were controlled after the reintroduction of infliximab or with the introduction of adalimumab,,,, certolizumab, azathioprine, methotrexate,, mesalazine and corticosteroids, or methotrexate and corticosteroids, demonstrating the considerable heterogeneity of approaches used after discontinuation of anti-TNF- therapy. Psoriatic lesions recurred in cases in which etanercept and adalimumab,, were given.
Recommended Reading: What Medicine To Take For Psoriasis
Psoriasiform Drug Eruption And Drug
âPsoriasiform drug eruptionâ is a broad term referring to a heterogeneous group of disorders that clinically and/or histologically simulate psoriasis at some point during the course of the disease. A psoriasiform eruption is used also to describe a histological reaction pattern, which exhibits presence of cellular infiltration, papillomatosis, and epidermal hyperplasia with elongation of rete ridges. Hypergranulosis and parakeratosis may also be observed in selected cases.â This type of eruption can also be seen with seborrheic dermatitis, pityriasis rubra pilaris, secondary syphilis, pityriasis rosea, mycosis fungoides, drugs, and some malignancies. These psoriasiform reactions are elicited by inflammatory events that cause dysregulation of cytokines, growth factors, and abnormal keratinocyte proliferation. Depending on the disorder, the lesions may vary in size, shape, extent and type of scaling, and anatomic distribution.
Data Extraction And Analysis
Two authors independently extracted data from each article, and disagreements were resolved by consensus. Each study was individually reviewed to identify data concerning age, gender, personal and family history of psoriasis, biological medication administered, duration of clinical latency, lesion type , performance of cutaneous biopsy, therapeutic approaches and outcomes, and clinical IBD development. Nonspecific or unavailable information was designated as unknown or unstated data. The selected data were compiled in Microsoft Excel. Because this information did not provide sufficient data evidence or meta-analysis data, a simple descriptive analysis was performed.
You May Like: What Kind Of Oil Is Good For Psoriasis
Pathophysiological Mechanisms Of Drug
The underlying mechanisms leading to drug-induced or drug-aggravated psoriasis are mostly incompletely understood. For some medications such as lithium, beta-blockers, and imiquimod, a direct drug effect is suspected., Alternatively, indirect mechanisms are sometimes implicated via a Koebner phenomenon, eg, in case of a drug hypersensitivity reaction, allergic reaction, irritant reaction, and phototoxicity.,
Several drugs have a well-described mode of action by which they can induce the development of psoriasis. Such mechanistic insights have helped to eludicate the pathophysiological pathways underlying psoriasis. One example is interferon-alpha, which plays an important role in the initiation of psoriasis. In psoriatic skin, activated plasmacytoid dendritic cells produce type I interferons, such as interferon-alpha, which in turn triggers a cascade leading to proinflammatory cytokine production. Similarly, exogenously administered interferon-alpha is able to induce Th1-and Th17-mediaded cutaneous inflammation.
Beta Blockers And Drug
Clinical manifestations of beta-blocker-provoked psoriasis. In the past, beta blockers have been known to cause drug-induced/exacerbation of psoriasis, psoriasiform dermatitis, eczematous eruptions, and lichenoid changes. Psoriasiform eruptions are the most common cutaneous consequence of beta-blocker therapy, seen more frequently in patients with no past or family history of psoriasis., Clinical improvement after withdrawal of the implicated drug is the distinguishing feature in many cases suggesting drug-induced psoriasis. In a case-controlled and case-crossover study of 110 patients who were hospitalized for extensive psoriasis vulgaris, beta blockers were considered a major factor in triggering or aggravating psoriasis.â Practolol is the prototype cardioselective beta blocker, which is no longer available due to the high incidence of cutaneous side effects reported, including psoriasiform eruptions and exacerbations of pre-existing psoriasis. Transformation of plaque-type psoriasis into pustular psoriasis with pindolol has also been observed. In addition, atenolol has been reported to precipitate psoriasiform pustulosis. Topical application of timolol in the treatment of open-angle glaucoma has been reported to induce psoriasis and to transform psoriasis vulgaris into psoriatic erythroderma through the passage into the systemic circulation via the conjunctiva.,
Also Check: Where Does Psoriasis Come From
Strategy For Article Search And Selection
We performed a systematic literature review by searching the Medline , Embase, Cochrane, SciELO, and LILACS databases for articles published from January 2004 to October 2011 . To identify all relevant articles published in English about psoriasis or psoriasiform lesions induced or exacerbated by TNF- antagonists in patients with IBD, we used the following search terms: adalimumab, anti-TNF-, biological, certolizumab, Crohn, inflammatory bowel disease, IBD, infliximab, TNF inhibitor, tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor, and ulcerative colitis combined with the terms adverse event, cutaneous adverse effects, exacerbated, guttate, new-onset, paradoxical, plaque, pustular psoriasis, side effect, and skin reactions. Relevant secondary references including abstracts published in the annals of national and international congresses were also included. Additionally, the reference lists of these articles were examined to identify additional studies. Repeated studies were considered only as a search source. Studies were selected based on their titles and retrieved for more detailed analysis. Theoretical review articles that did not include additional cases were excluded, as were studies that did not present information about IBD separately from other diseases. Principles of the PICO strategy were adopted to ensure quality.
Controversies About Psoriasis Induced / Aggravated By Drugs
Psoriasis is a very common disease, and its exacerbation / induction attributed to a drug has been suggested to be coincidental. There are some clinical controversies about the true appearance of a psoriasis triggered by drugs. In fact, skin eruptions in some cases do not appear to be typical psoriasis and are described as psoriasiform. These psoriasiform reactions are less red, less thick, and less scaly, and the knees and elbows tend not to be involved. Another problem is that uninvolved skin of patients with psoriasis responds to various stimuli and an adverse drug reaction in a psoriatic background may present with psoriasis via a Koebner response. In addition, psoriasis may be induced by other triggers. For instance, it has been suggested that the worsening or induction of psoriasis in the setting of an antibiotic therapy may be because of the infection and not the use of the antibiotics.
We performed a study at the Section of Dermatology of the University of Genoa on 85 patients with a new diagnosis of psoriasis compared with 85 matched controls attending our clinic for different cutaneous surgical procedures for evaluating a significant difference in drug intake. No significant difference between the 2 groups was found concerning the intake of antihypertensive drugs.
Also Check: Natural Treatment For Psoriasis Dr Axe
What Are The Clinical Features Of Drug
Drug-induced or drug-aggravated psoriasis may induce:
- Localisedplaque psoriasis, often affecting scalp, knees, elbows, buttocks and/or genitals
- Generalised plaque psoriasis, with scattered plaques on all parts of the body
- Erythroderma when the entire skin surface is red and scaly.
Acute generalised exanthematouspustulosis is a severe drug-induced eruption that closely resembles generalised pustular psoriasis.
Palmoplantar pustulosis can also be drug-induced, often by tumour necrosis factor inhibitors. Although closely related, palmoplantar pustulosis is no longer classified as a type of psoriasis. It nearly always occurs in smokers.
Histopathological Features Of Drug
There are few systematic studies on the histopathology of drug-induced psoriasis. In most cases, the histopathology of a drug-induced psoriasis is virtually indistinguishable from that of conventional psoriasis. However, drug-induced psoriasis often lacks tortuous papillary dermal capillaries and associated suprapapillary epidermal thinning, which may be used as differential criterion. Furthermore, the number of Munro micro-abscesses and macrophages may be low in drug-related psoriasis. Additional histological clues to diagnose a potential drug-induced psoriasis include an eosinophilic infiltrate in the dermis and a lichenoid pattern.,, Importantly, however, absence of these histopathological findings does not exclude the possibility of a drug-related psoriasis.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Treat Plaque Psoriasis
Psoriasiform Drug Eruption Associated With Sodium Valproate
Gulen Gul Mert
1Division of Pediatric Neurology, Department of Pediatrics, Cukurova University, 01180 Adana, Turkey
2Department of Dermatology, Cukurova University, 01180 Adana, Turkey
Academic Editor:
Abstract
As psoriasis is a common skin disorder, knowledge of the factors that may induce, trigger, or exacerbate the disease is of primary importance in clinical practice. Drug intake is a major concern in this respect, as new drugs are constantly being added to the list of factors that may influence the course of the disease. We report a patient with a psoriasiform drug eruption associated with the use of sodium valproate. Physicians should be aware of this type of reaction. Early detection of these cases has practical importance since the identification and elimination of the causative drug are essential for therapy success.
1. Introduction
2. Case
A 16-year-old boy who had epilepsy and mental retardation secondary to hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy was put on sodium valproate 500mg twice a day for generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Approximately three months after starting sodium valproate, he presented with a psoriasiform eruption on his limbs and trunk. He had not taken any other medication, and he had no personal or family history of psoriasis. Routine laboratory investigations including complete blood cell count, liver and renal function tests, urinalysis were within normal limits.
3. Discussion
References
What Causes Drug
The most common drugs to induce or aggravate psoriasis are:
- -blockers
- Lithium and less often, other medications that are given to improve mood
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs including indomethacin and aspirin
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
Other common triggers for psoriatic exacerbations include trauma, sunburn, streptococcal infection, human immunodeficiency virus infection and emotional stress.
Read Also: Does Red Light Therapy Help Psoriasis
Who Gets Drug
As with psoriasis that is not induced by a drug, drug-induced psoriasis occurs more frequently in patients with a history of:
- Obesity
- Dyslipidaemia .
Other risk factors for psoriasis include:
- Race psoriasis occurs in all races, but it is more common in Caucasians than in those of African descent
- A family history of psoriasis
- Age the most common ages for the onset of psoriasis are 1622 years and 5760 years.
What Is Drug
In some people, psoriasis is drug-induced or drug-aggravated.
- In drug-induced psoriasis, discontinuation of the offending drug leads to the clearance of psoriasis. It occurs in patients with no previous history of psoriasis.
- In drug-aggravated psoriasis, the disease continues to develop even after the causative drug has been discontinued. It typically occurs in patients with a personal or family history of psoriasis.
These forms of psoriasis differ from psoriasiformdrug eruption, a group of papular drug eruptions characterised histologically by epidermalhyperplasia and hypergranulosis.
Psoriasis induced by lithium
Don’t Miss: What Vitamins Should I Take For Psoriasis
How Is Drug
Diagnosis of drug-induced psoriasis can be challenging when patients are on multiple medications. The onset of psoriatic symptoms can be months or years after the drug has been started. Careful patient history is essential in any patient that presents with new-onset psoriasis and must include their current medications. The possibility of other triggers for psoriasis, apart from drugs, should also be taken into consideration.